| Apr 18, 2024 |
|
(Nanowerk News) In a paper published in Device (“Efficient energy generation from a sweat-powered, wearable, MXene-based hydroelectric nanogenerator”), Deakin researchers have outlined how they have designed a ground-breaking wearable hydroelectric nanogenerator – powerful enough to power small electronics such as Fitbits and smart watches – that combines conductive nanomaterials and the evaporation of sweat to generate and store electrical power.
|
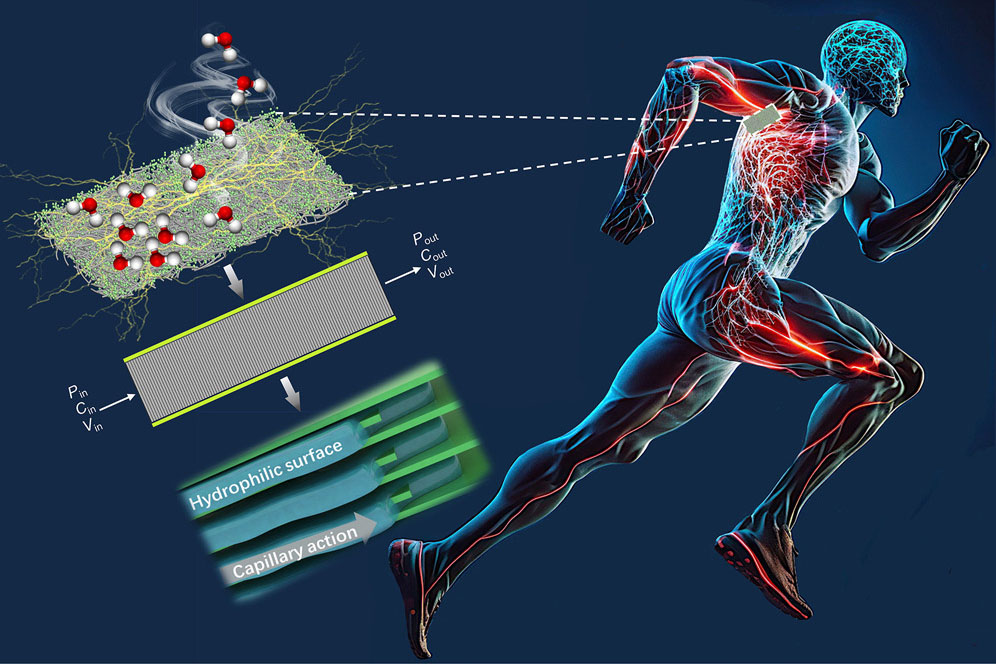 |
| IFM researchers have designed a new hydroelectric nanogenerator for wearable electronics that integrates a single-layer MXene nanosheet with wool as the electrochemically active component. (Image: IFM)
|
|
In the past, the mechanics of hydroelectric nanogenerators were little understood and had several shortcomings, including lower power output density, however this new technology integrates a single-layer MXene nanosheet with wool as the electrochemically active component.
|
|
‘Imagine a tiny device that you could wear, like a bracelet or headband, that could generate electricity from something as simple as your sweat,’ research co-author IFM Associate Professor Jingliang Li said.
|
|
‘The device only needs a small amount of sweat to operate – only few drops to cover the surface of the device.
|
|
‘Operation-wise a device needs sweat to generate the current, but since the device is attached to a capacitor, the generated current can be stored. This does not require the wearer to sweat continuously.
|
|
‘Similar to a solar panel generating electricity, the generated current can be gradually stored in another device.’
|
|
This breakthrough research – led at IFM by Associate Professor Li, Dr Azadeh Nilghaz and PhD candidate Hongli Su – could provide a greener, and low maintenance alternative to meet that demand.
|
|
Further development is needed before the technology could be commercialised for public sale; however, the device shows promise of being easy and low-cost to fabricate.
|
|
Looking ahead, the research team hopes to explore how the device can generate electricity if they don’t sweat.
|
|
‘The device can generate electricity from the moisture produced by breathing,’ Associate Professor Li said. ‘This is our future work.’
|


