Tire Pressure Monitoring System Reference Design
The TPM reference design uses a base station, LF initiator, and tire sensors to keep vehicles safe and efficient, communicating through LIN and CAN networks.
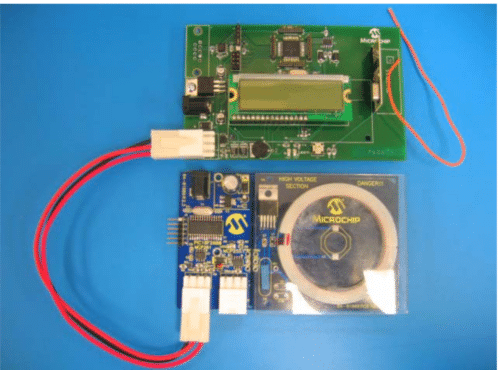
The Tire Pressure Monitoring (TPM) System is essential for enhancing safety and improving vehicle efficiency. Proper tire pressure is vital for safe driving, as underinflated tires can lead to dangerous tire failures, such as blowouts, potentially causing accidents. The TPM system alerts drivers to such conditions, allowing them to correct the issue promptly. Additionally, correct tire pressure ensures that vehicles operate with optimal fuel efficiency. Underinflated tires increase rolling resistance, which forces the engine to consume more fuel. By maintaining proper tire pressure, the TPM system helps reduce fuel consumption and extends the life of the tires by preventing uneven wear. This not only saves on fuel costs but also reduces the frequency of tire replacements, further emphasizing the importance of tire pressure monitoring in modern vehicles.
The reference design of TPM from Microchip consists of a base station, a low-frequency initiator, and tire sensors. The Base Station activates the sensor modules in each tire using the Low Frequency Initiator to gather data on pressure, temperature, and battery level sequentially. This process is facilitated over the LIN network, where the Base Station sends commands to the LF Initiator. Subsequently, the LF Initiator sends a wake-up challenge to the tire sensor modules using a 125 kHz ASK modulated signal. The Tire Sensor module’s 3-axis Analog Front End (MCP2030) verifies the challenge and wakes the microcontroller from sleep only if the preambles align. Following activation, the sensor module measures the pressure and temperature, checks the battery status, and transmits this data back to the Base Station via a 433.9 MHz signal. The Base Station then displays the information on an LCD.
The Base Station, equipped with a PIC18F4680 and including MCP201 LIN Transceiver and MCP2551 CAN Transceiver, handles communications over LIN or CAN networks. The LF Initiator module utilizes a PIC18F2680 and also features these transceivers for robust data communication. Meanwhile, the Tire Sensor module built around a PIC16F684 microcontroller employs the MCP2030 AFE to detect the 125KHz signal and includes analog sensors for accurate pressure and temperature measurements. This setup supports RF protocols (UHF and 125KHz), contributing to its low power consumption and reliable signal detection. The flexibility of this system makes it a robust choice for ensuring vehicle safety and efficiency across various tire monitoring applications.
The module utilizes a microcontroller that is selected for its comprehensive feature set, including a CAN controller and a LIN-compatible EUSART, allowing it to interface efficiently with in-vehicle networks. Additionally, the module incorporates a UHF receiver which features an AM super-regenerative compact hybrid module to capture decoded data from an AM transmitter. This receiver offers high frequency stability across a broad range of operating temperatures and is robust against mechanical vibrations or manual handling. It also includes a laser-trimmed onboard inductor, eliminating the need for adjustable components, thus simplifying the design and enhancing reliability.
Microchip has tested this reference design. It comes with a Bill of Material (BOM), schematics, etc. You can find additional data about the reference design on the company’s website. To read more about this reference design, click here.


